Asia-Pacific Japanese Restaurant Market Flourishes with Rising Popularity of Japanese Cuisine
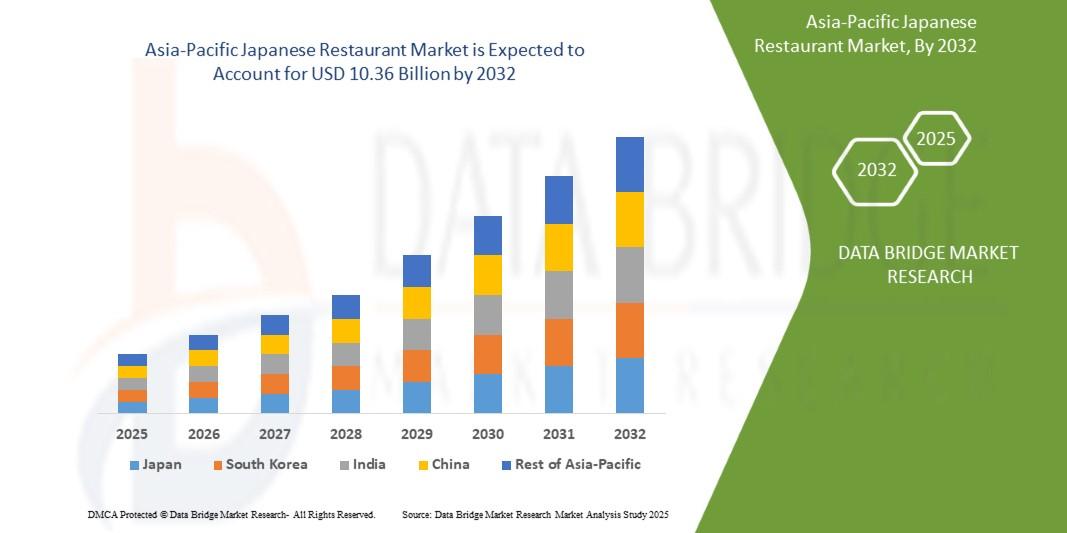
The Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market has emerged as one of the most dynamic and fast-evolving segments within the regional foodservice industry. Rooted in centuries-old culinary traditions yet continuously adapting to modern tastes, Japanese cuisine has achieved widespread acceptance across both developed and emerging Asia-Pacific economies. From sushi bars and ramen shops to premium fine-dining concepts, Japanese restaurants are expanding rapidly, supported by changing consumer lifestyles, rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and the growing influence of Japanese pop culture.
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market, exploring its growth drivers, key market segments, consumer behavior trends, operational challenges, and future outlook.
Uncover strategic insights and future opportunities in the Asia-Pacific Japanese Restaurant Market. Access the complete report:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/asia-pacific-japanese-restaurant-market
Market Overview
The Asia-Pacific region represents a diverse and fertile ground for Japanese restaurant growth. Countries such as Japan, China, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Thailand, Indonesia, and India are witnessing strong demand for Japanese dining experiences. While Japan remains the cultural and culinary origin of the cuisine, international-style Japanese restaurants in other Asia-Pacific countries are often localized to suit regional palates, pricing sensitivities, and dining habits.
Japanese restaurants are generally perceived as offering high-quality, aesthetically appealing, and relatively healthy food options. This perception has significantly boosted their popularity among health-conscious urban consumers, young professionals, and millennials. Additionally, the expansion of shopping malls, business districts, airports, and hospitality hubs across Asia-Pacific has created ideal locations for Japanese restaurant chains and independent operators alike.
Key Growth Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market is the increasing demand for international and premium dining experiences. As middle-class populations expand across Asia-Pacific, consumers are more willing to spend on experiential dining rather than just basic meals. Japanese cuisine, known for its presentation, flavor balance, and cultural authenticity, fits well into this trend.
Another major growth factor is the rising awareness of healthy eating. Traditional Japanese food emphasizes fresh ingredients, seafood, vegetables, fermented products, and controlled portion sizes. Dishes such as sushi, sashimi, miso soup, and grilled fish align with consumer preferences for low-fat, high-protein, and nutrient-rich meals, giving Japanese restaurants a competitive advantage over fast-food outlets.
The influence of Japanese culture, including anime, manga, fashion, and tourism, has also played a crucial role in market expansion. Many Asia-Pacific consumers are introduced to Japanese cuisine through travel, media exposure, and cultural events, which increases familiarity and demand. Furthermore, the growth of Japanese expatriate communities and multinational corporate presence has supported consistent demand for authentic Japanese dining options.
Market Segmentation
The Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market can be segmented by restaurant type, service format, and price range.
By restaurant type, the market includes sushi restaurants, ramen shops, izakayas, teppanyaki restaurants, yakiniku outlets, and multi-cuisine Japanese fusion restaurants. Sushi and ramen segments dominate due to their strong brand recognition, scalability, and adaptability to quick-service or casual dining formats.
By service format, Japanese restaurants are categorized into quick service restaurants, casual dining restaurants, and fine dining establishments. Quick service and casual dining formats are experiencing faster growth, driven by urban lifestyles, busy work schedules, and the increasing popularity of food delivery platforms. Fine dining Japanese restaurants, while smaller in number, maintain strong demand among affluent consumers and corporate clientele.
By price range, the market spans affordable mass-market outlets to premium and luxury dining experiences. Affordable Japanese chains are expanding rapidly in emerging Asia-Pacific markets, while premium concepts thrive in metropolitan cities and tourist destinations.
Consumer Trends and Preferences
Consumer behavior in the Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market is evolving rapidly. One notable trend is the growing preference for customization and localized flavors. While authenticity remains important, many restaurants adapt their menus by incorporating regional spices, vegetarian options, and fusion dishes to cater to local tastes.
Another key trend is the rise of vegetarian and plant-based Japanese offerings. With increasing numbers of flexitarian and vegetarian consumers in countries such as India, Australia, and parts of Southeast Asia, Japanese restaurants are introducing vegetable sushi, tofu-based dishes, and plant-based ramen broths.
Digitalization is also reshaping the market. Online food delivery, digital menus, mobile ordering, and loyalty programs have become essential tools for customer acquisition and retention. Japanese restaurants that leverage social media marketing and visually appealing food presentation often gain strong brand visibility, particularly among younger consumers.
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are gaining importance as well. Consumers are becoming more conscious of seafood sourcing, waste reduction, and eco-friendly packaging. Restaurants that communicate sustainability initiatives tend to build stronger brand trust and customer loyalty.
Competitive Landscape
The Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market is highly competitive and fragmented, with a mix of global chains, regional brands, and independent operators. International Japanese restaurant chains are expanding through franchising and joint ventures, particularly in Southeast Asia and Australia. At the same time, local entrepreneurs are launching homegrown Japanese concepts that blend authenticity with regional innovation.
Competition is not limited to other Japanese restaurants but also includes Korean, Chinese, Western, and pan-Asian dining concepts. To differentiate themselves, Japanese restaurants focus on menu innovation, interior design, service quality, and brand storytelling. Chef-led concepts and experiential dining formats such as open kitchens and live teppanyaki counters are increasingly popular.
Challenges and Constraints
Despite strong growth prospects, the Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market faces several challenges. High operating costs, including premium ingredients, skilled chefs, and imported supplies, can impact profit margins. Authentic Japanese ingredients such as seafood, sauces, and seasonings may face supply chain disruptions or price volatility.
Another challenge is maintaining consistency and authenticity while scaling operations across multiple locations and countries. Recruiting and retaining trained Japanese chefs or staff familiar with traditional techniques can be difficult, particularly in emerging markets.
Additionally, intense competition and changing consumer expectations require continuous innovation. Restaurants that fail to adapt to digital trends, dietary preferences, or value-for-money considerations may struggle to sustain long-term growth.
Future Outlook
The future of the Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market appears highly promising. Continued urbanization, tourism recovery, rising disposable incomes, and growing interest in global cuisines are expected to support steady market expansion. Emerging markets in Southeast Asia and South Asia are likely to offer significant growth opportunities, particularly for affordable and mid-range Japanese dining concepts.
Innovation in menu offerings, technology adoption, and sustainability practices will be critical success factors. Restaurants that balance authenticity with localization, quality with affordability, and tradition with modern dining experiences are expected to gain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, the Asia-Pacific Japanese restaurant market stands at the intersection of tradition and transformation. With strong consumer demand, cultural appeal, and evolving dining trends, Japanese restaurants are set to remain a vital and influential part of the Asia-Pacific foodservice landscape for years to come.
Browse More Reports:
Global Water Treatment Chemicals Market
Global Scented Candle Market
Global Ceramics Market
Europe Japanese Restaurant Market
Global Smart Fleet Management Market
Global Tuna Market
Global Tote Bags Market
Global Gemstones Market
Global Japanese Restaurant Market
Global Hypochlorous Acid Market
Global Toothbrush Market
Global Cataracts Market
Global Wire and Cable Market
Global Plant-Based Food Market
Global Tomatoes Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- corporatesales@databridgemarketresearch.com






