Leg Cramps: Understanding, Relieving, and Preventing Them
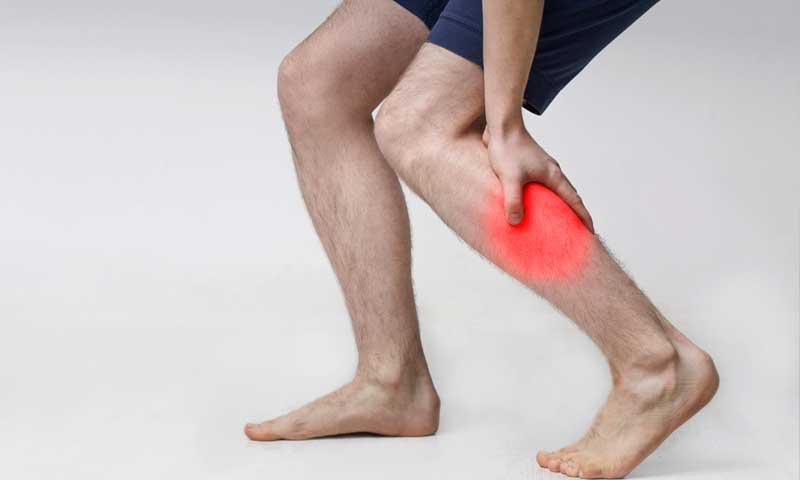
Leg cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions of the muscles in your legs that can cause sharp pain and discomfort. They often occur in the calves, thighs, or feet and can strike during the day or at night, disrupting daily activities or sleep. While leg cramps are usually harmless, they can be painful and frustrating, especially when they happen frequently.
Understanding the causes of leg cramps, how to relieve them, and steps to prevent them can help you manage this common condition effectively. This article provides practical guidance in simple, human-friendly language suitable for general readers.
What Are Leg Cramps?
A leg cramp is an involuntary tightening or spasm of a muscle. These contractions can last from a few seconds to several minutes and can vary in intensity. Most leg cramps affect the calf muscles, but they can also occur in the thighs, hamstrings, or feet.
Key features of leg cramps:
-
Sudden, sharp pain
-
Muscle hardening or knotting
-
Temporary restriction of movement
-
Commonly occur at night or after physical activity
Leg cramps are generally not a sign of a serious medical condition, but frequent or severe cramps may warrant medical attention.
Common Causes of Leg Cramps
Leg cramps can result from various factors, often linked to lifestyle, activity, or underlying health conditions.
1. Muscle Fatigue or Overuse
Excessive exercise, prolonged standing, or sudden increases in physical activity can strain muscles and trigger leg cramps.
2. Dehydration
Insufficient water intake can disrupt the balance of electrolytes, such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium, leading to muscle contractions.
3. Nutrient Deficiencies
Low levels of essential minerals like potassium, calcium, or magnesium may increase the likelihood of leg cramps.
4. Poor Circulation
Conditions affecting blood flow in the legs, such as peripheral artery disease, can contribute to cramping, especially during activity.
5. Medications
Some medications, including diuretics, statins, or certain blood pressure drugs, may increase the risk of leg cramps.
6. Pregnancy
Pregnant individuals often experience leg cramps due to changes in blood circulation, weight gain, and nutrient demands.
7. Aging
As muscles naturally lose mass and flexibility with age, leg cramps may become more common.
How to Relieve Leg Cramps
Immediate relief during a leg cramp can be achieved through gentle stretching and care.
Effective Relief Techniques
-
Stretch the Muscle: If the cramp is in the calf, straighten your leg and gently pull your toes toward your head.
-
Massage: Rub the affected muscle to relax the tight fibers.
-
Heat Therapy: Apply a warm towel or heating pad to the muscle to ease tension.
-
Cold Therapy: Ice packs may reduce soreness after the cramp subsides.
-
Walk or Move Gently: Light movement can restore normal blood flow and help the muscle relax.
Hydrating and replenishing electrolytes after a cramp can also help reduce future occurrences.
Prevention Tips for Leg Cramps
Preventing leg cramps involves addressing common triggers through lifestyle adjustments and habits.
1. Stay Hydrated
Drink water consistently throughout the day, especially during exercise or hot weather, to maintain electrolyte balance.
2. Stretch Regularly
Incorporate stretching routines for calves, hamstrings, and thighs into your daily activities or before and after exercise.
3. Maintain a Balanced Diet
Eat foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and dairy can support muscle function.
4. Exercise Smartly
Gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activity. Avoid sudden strain or overexertion.
5. Wear Proper Footwear
Supportive shoes with proper arch support reduce muscle strain during daily activity or exercise.
6. Improve Circulation
Take short breaks from sitting, elevate legs when resting, and perform gentle leg exercises to encourage blood flow.
7. Adjust Sleeping Position
If cramps occur at night, stretching before bed and avoiding prolonged pressure on muscles can help.
When to See a Doctor
Leg cramps are usually harmless, but you should seek medical attention if:
-
Cramps occur frequently or severely
-
Pain persists after the cramp resolves
-
There is swelling, redness, or warmth in the leg
-
You notice numbness or weakness
These symptoms may indicate an underlying medical condition requiring professional evaluation.
Lifestyle Habits to Support Muscle Health
Supporting muscle and leg health overall can reduce the frequency of cramps.
Tips for Healthy Legs
-
Regular Exercise: Include strength training and flexibility exercises for legs.
-
Hydration: Keep fluids consistent throughout the day.
-
Balanced Nutrition: Incorporate vitamins and minerals essential for muscle function.
-
Avoid Excessive Alcohol or Caffeine: Both can contribute to dehydration and cramping.
-
Manage Stress: Chronic tension can worsen muscle discomfort.
Understanding Nighttime Leg Cramps
Many people experience leg cramps while sleeping. These nighttime leg cramps can be particularly disruptive. Factors contributing to nighttime cramps include:
-
Extended periods of inactivity during sleep
-
Poor sleeping posture
-
Dehydration or low mineral levels
-
Age-related muscle changes
Gentle stretching before bedtime, staying hydrated, and maintaining a comfortable sleeping position can help reduce nighttime leg cramps.
The Role of Electrolytes
Electrolytes like potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium are critical for muscle contraction and relaxation. An imbalance can trigger muscle spasms and leg cramps.
Foods to Support Electrolyte Balance
-
Bananas, oranges, and other fruits (potassium)
-
Leafy greens and nuts (magnesium)
-
Dairy products (calcium)
-
Moderate salt intake for sodium balance
A balanced diet with a variety of nutrient-rich foods helps maintain proper muscle function.
Summary: Managing and Preventing Leg Cramps
Leg cramps are common but manageable with proper care. Understanding triggers, stretching regularly, staying hydrated, eating a nutrient-rich diet, and maintaining a consistent exercise routine can reduce discomfort and frequency.
Key takeaways:
-
Leg cramps are sudden, involuntary muscle contractions.
-
Common causes include dehydration, overuse, poor circulation, and nutrient deficiencies.
-
Immediate relief comes from stretching, massage, and gentle movement.
-
Prevention involves hydration, nutrition, stretching, and proper footwear.
-
Seek medical advice if cramps are severe, frequent, or accompanied by unusual symptoms.
By incorporating simple daily habits, leg cramps can be minimized, improving comfort, mobility, and quality of life.
الأقسام
إقرأ المزيد
The Global Data Center Colocation Market Report presents an in-depth analysis, merging qualitative and quantitative insights to provide a holistic understanding of the market's dynamics. The report evaluates growth drivers, challenges, and constraints while forecasting revenue trends across key segments. It offers both historical and projected data, giving stakeholders a clear view of market...

In an increasingly connected world, travelers expect uninterrupted access to mobile data and phone services wherever they go. From international business trips to leisure travel, connectivity has become essential for navigation, communication, and productivity. eSIMo answers this global demand by offering an advanced digital connectivity solution that removes the complexity of traditional SIM...

Global construction repainting continues to evolve with significant technological advancements, offering enhanced performance and broader application benefits. Modern coatings are designed to deliver superior protection, resist harsh climates, and improve both interior and exterior aesthetics. Repainting cycles are also influenced by lifestyle changes, rising renovation investments, and greater...

Understanding Material Characteristics Before using metallic decorative film, it is important to understand its basic material properties. These Metallic Decorative Film often combine a plastic base with a metallic surface layer or coating. While they provide an attractive appearance, they may have different flexibility, heat resistance, and surface hardness compared to standard films....

The gripping saga of Emilia Urquiza will continue. Netflix has officially greenlit a second season of its original series 'Ingobernable'. This renewal follows the global audience's deep investment in Kate del Castillo's portrayal of the First Lady. Her fight for justice and the complex web of political intrigue left viewers demanding answers. The new season is slated to premiere in 2018,...


