Blood Sugar Levels: Understanding and Maintaining Healthy Glucose
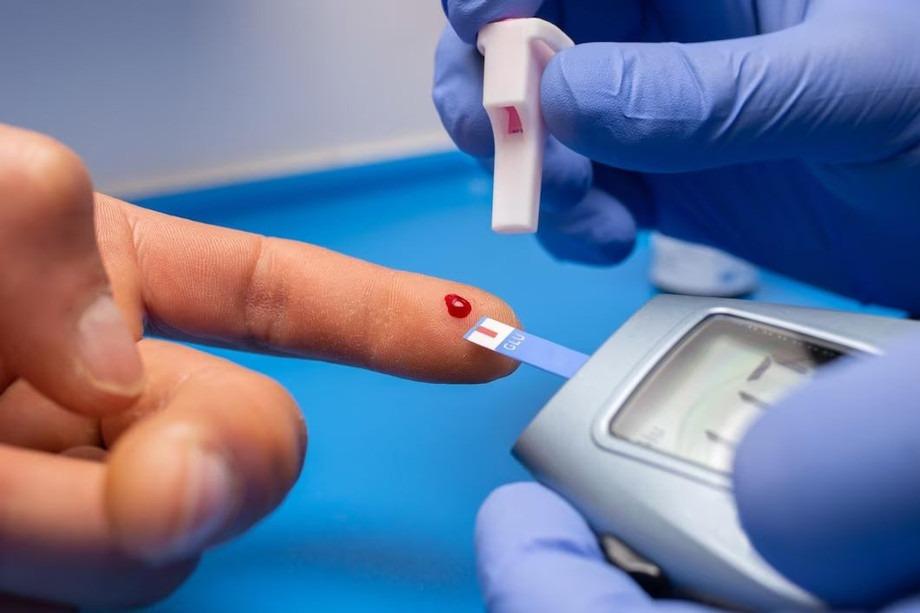
Blood sugar levels, also known as glucose levels, are a key indicator of overall health. Glucose is the main source of energy for your body, providing fuel for the brain, muscles, and other organs. Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is essential for energy, mood, and long-term health.
High or low blood sugar levels can lead to short-term discomfort and, over time, contribute to serious health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and nerve damage. Understanding how blood sugar works, what affects it, and how to maintain balance can help you lead a healthier life.
What Are Blood Sugar Levels?
Blood sugar levels refer to the amount of glucose present in your bloodstream at any given time. Glucose comes from the food you eat, particularly carbohydrates, and is used by your body for energy.
The body regulates blood sugar through insulin and other hormones, which help move glucose from the blood into cells. Proper regulation keeps blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Why Blood Sugar Levels Matter
Stable blood sugar levels are crucial because they:
-
Provide consistent energy throughout the day
-
Support brain function and concentration
-
Help maintain a healthy metabolism
-
Reduce the risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes
Frequent spikes or drops in blood sugar can cause fatigue, irritability, and difficulty focusing. Over time, uncontrolled blood sugar levels may damage organs and tissues.
Common Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors influence blood sugar levels, including lifestyle, diet, and overall health.
1. Diet and Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates directly impact blood sugar levels because they are broken down into glucose. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as sugary snacks and refined grains, can cause rapid spikes.
2. Physical Activity
Exercise helps lower blood sugar by allowing muscles to use glucose for energy. Both aerobic exercise and strength training contribute to improved glucose regulation.
3. Stress and Hormones
Stress triggers the release of cortisol, which can increase blood sugar levels. Chronic stress may contribute to long-term imbalances.
4. Sleep Patterns
Insufficient sleep can affect insulin sensitivity and lead to higher blood sugar levels. Consistent, quality sleep supports glucose balance.
5. Medical Conditions and Medications
Certain conditions, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, or hormonal imbalances, can impact blood sugar. Some medications may also affect glucose levels.
Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
While exact numbers vary based on age and health status, general guidelines for fasting blood sugar levels are:
-
Normal: 70–99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter)
-
Prediabetes: 100–125 mg/dL
-
Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
Post-meal blood sugar levels are generally considered normal if they stay below 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps identify trends and prevent complications.
Signs of Blood Sugar Imbalance
Imbalances in blood sugar can cause noticeable symptoms.
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
-
Frequent urination
-
Increased thirst
-
Fatigue
-
Blurred vision
-
Headaches
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
-
Shakiness or dizziness
-
Sweating
-
Hunger
-
Confusion or difficulty concentrating
-
Rapid heartbeat
Recognizing these signs early allows you to take action and restore balance.
Tips to Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels involves a combination of diet, exercise, lifestyle habits, and mindfulness.
1. Balanced Diet
Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods. Include:
-
Vegetables and fruits
-
Whole grains
-
Lean proteins
-
Healthy fats such as nuts, seeds, and olive oil
Limit highly processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Aim for consistent movement throughout the week. Activities like walking, swimming, cycling, and resistance training help the body use glucose efficiently.
3. Portion Control
Overeating, even healthy foods, can raise blood sugar levels. Eating smaller, balanced meals throughout the day supports steady glucose.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water helps your kidneys remove excess glucose from the bloodstream and supports overall metabolism.
5. Stress Management
Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or hobbies that help you relax. Lower stress levels support more stable blood sugar.
6. Adequate Sleep
Prioritize 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night. Good sleep improves insulin sensitivity and helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
7. Regular Monitoring
For individuals at risk of diabetes or with known blood sugar issues, monitoring levels with a glucometer can provide useful feedback and guide lifestyle adjustments.
Foods That Support Blood Sugar Balance
Certain foods help regulate blood sugar levels naturally:
-
Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens provide fiber and micronutrients.
-
Whole grains: Oats, quinoa, and brown rice have a slower impact on glucose.
-
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas provide protein and fiber.
-
Fruits: Berries, apples, and citrus fruits offer vitamins and antioxidants.
-
Healthy fats: Avocado, olive oil, and nuts help slow sugar absorption.
Pairing carbohydrates with protein or healthy fat slows digestion and helps keep blood sugar levels steady.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Control
Long-term blood sugar management is about consistent habits rather than short-term fixes.
-
Eat consistently: Avoid skipping meals to prevent sugar spikes and crashes.
-
Stay active: Incorporate both cardio and strength exercises weekly.
-
Maintain healthy weight: Reduces insulin resistance and supports glucose control.
-
Limit alcohol and tobacco: Both can interfere with blood sugar regulation.
-
Plan meals mindfully: Choose complex carbs, fiber, and balanced portions.
These adjustments can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications related to unstable blood sugar levels.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Routine health check-ups are essential to monitor blood sugar levels and overall health. Early detection of imbalances allows for effective lifestyle adjustments and medical guidance if necessary.
Summary
Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in overall health, energy, and wellbeing. Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels involves a combination of diet, exercise, stress management, hydration, and sleep. Recognizing symptoms of imbalance, eating a nutrient-rich diet, and adopting consistent lifestyle habits can help prevent complications and promote long-term wellness.
By understanding how blood sugar works and taking proactive steps, you can maintain stable glucose levels and support your overall health naturally.
Categorias
Leia mais
In a surprise pivot away from the indie darlings favored by many critics, the Producers Guild of America nominated big-budget studio features for its best-picture slate. The five finalists are A Beautiful Mind; Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone; The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring; Moulin Rouge; and Shrek. Collectively those films have earned roughly $900 million at the...

在現今數位化快速發展的時代,線上遊戲與娛樂平台已成為許多人休閒娛樂的重要選擇。其中,yygaming 憑藉其豐富的遊戲內容、創新的互動體驗以及穩定的服務品質,逐漸成為玩家心中的首選。不論是喜愛棋牌遊戲的玩家,還是追求刺激競技的愛好者,yygaming 都能提供全方位的娛樂享受。 為什麼選擇 yygaming? yygaming 不僅僅是一個線上遊戲平台,它更是一個集合多樣娛樂的數位社群。以下幾點特色,讓它在眾多平台中脫穎而出: 多元化遊戲選擇:從經典的棋牌遊戲、電子競技到即時互動娛樂,滿足不同玩家的需求。 穩定流暢的系統:先進的技術支援,確保玩家在遊戲過程中不受延遲或中斷困擾。 高安全保障:平台採用嚴格的加密技術,確保玩家帳號與資金安全。 使用者體驗友好:簡潔的介面設計與直覺化操作,讓新手也能快速上手。 yygaming 的遊戲亮點...

I train most days with back-to-back sessions, mixing runs, gym lifts, and quick home circuits, and vaping is one small thing that helps me manage nicotine without losing focus. Lately I have been using strawberry lemonade vape juice during those packed workout days because the flavor stays consistent no matter how long or intense the session gets. The strawberry comes through sweet but never...

High-Quality CNC Tools for Professionals – Complete Buying Guide In the current competitive manufacturing environment, accuracy is essential. Juxtaposing a state-of-the-art machining shop to a garage, the cutting tools that you select will be the first in a line of inquiries on the quality of parts that it will produce, production rates, and performance. This is the reason for all...

What’s Fueling Executive Summary Welding Products Market Size and Share Growth The global welding products market size was valued at USD 15.47 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 23.27 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 5.23% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2032. An influential Welding Products Market document supports in achieving a sustainable growth in the...


