How Does a Radius Gauge Help in Workshop Measurement?
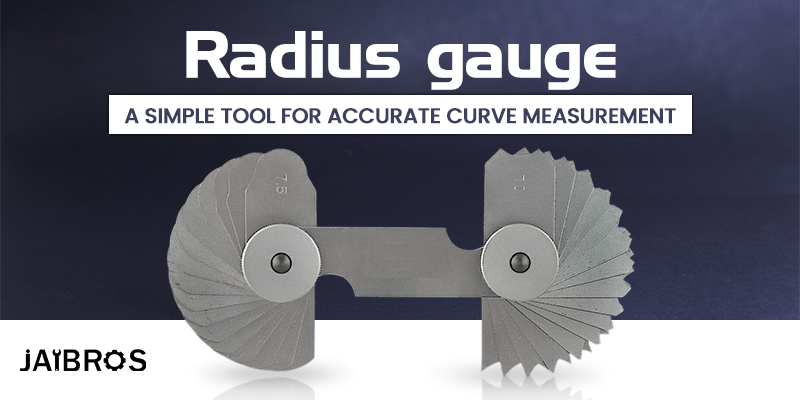
A simple guide explaining radius gauge, its working, least count, size range, and role in accurate workshop measurement.
What Is a Radius Gauge?
A radius gauge is a precision measuring tool used to check the radius of curved surfaces. It helps identify whether a curve is concave or convex and measures its exact size. This tool does not give digital readings but works by matching the curve of the gauge leaf with the curve of the workpiece.
Each gauge consists of several thin metal leaves. Every leaf has a different radius value marked on it. When a leaf fits perfectly on a curved edge without gaps or light passing through, that radius value is considered correct.
This tool is commonly used on shafts, fillets, grooves, dies, moulds, and machined components where curved edges are required.
Why Radius Measurement Is Important
In machining and manufacturing, even a small error in radius can cause major problems. Incorrect radii can lead to stress concentration, poor surface finish, vibration, or assembly failure. Proper radius measurement ensures that parts fit well, reduce wear, and improve safety.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, tool making, and general engineering depend on accurate radius checking for consistent quality.
Types of Radius Gauges
There are mainly two types based on curve shape. One is used for checking outer curves, known as convex radius measurement. The other is used for checking inner curves, known as concave radius measurement. Many gauge sets include both types together.
Some sets have separate leaves for internal and external radii, while others combine both shapes on the same leaf. The choice depends on the application and user requirement.
Radius Gauge Set and Construction
A standard radius gauge set contains multiple leaves fixed together using a screw or rivet. Each leaf is made from hardened stainless steel or spring steel for durability and accuracy. The leaves are thin so they can fit into small curves and narrow grooves.
Each leaf is clearly marked with its radius value, usually in millimetres. The leaves can be rotated out individually for checking and folded back after use for safe storage.
Radius Gauge Size Range
Radius gauge size depends on the number of leaves in the set. Common sets start from very small sizes like 1 mm and go up to 7 mm or more. Some larger sets may include sizes up to 25 mm or even higher.
Smaller radius sizes are mostly used in precision machining and tool making, while larger sizes are used in fabrication and general engineering work. Choosing the correct size range is important to cover your regular workshop needs.
Least Count of Radius Gauge
The least count of a radius gauge depends on the smallest difference between two consecutive leaves. In most standard metric sets, the least count is 0.5 mm. This means the tool can measure radius values in steps of 0.5 mm.
For higher accuracy needs, some fine sets have a least count of 0.25 mm. While this tool does not give numerical readings like vernier instruments, its accuracy depends on visual matching and user skill.
Radius Gauge Specification
Typical radius gauge specification includes material, size range, number of leaves, and accuracy level. Most gauges are made from hardened stainless steel to resist wear and corrosion. The accuracy usually falls within workshop tolerance limits suitable for machining and inspection.
The leaves are ground smoothly to ensure proper contact with the surface being measured. Clear laser or stamped markings help users read values easily even after long use.
How to Use a Radius Gauge Correctly
To use the tool, first clean the surface of the workpiece. Dirt or oil can affect accuracy. Select a leaf that looks close to the curve size. Place it against the curved surface gently.
If there is a visible gap or light passing through, try another leaf. The correct leaf will match the curve perfectly without rocking or gaps. Do not force the leaf, as it can damage both the gauge and the workpiece.
Good lighting improves accuracy when checking the fit.
Applications in Workshops
This measuring tool is widely used in CNC machining, lathe work, milling operations, and grinding jobs. Tool makers use it to check cutter profiles and die radii. Quality inspectors use it during final inspection before assembly.
It is also commonly used in training institutes to teach students about profile measurement and basic inspection techniques.
Care and Maintenance
Proper care helps maintain accuracy for a long time. Always clean the leaves after use and store them in a dry place. Avoid dropping the gauge, as thin leaves can bend easily.
Do not use the gauge for purposes other than measurement, such as scraping or prying. Regular inspection of leaf edges helps identify wear or damage early.
Advantages and Limitations
The main advantage of this tool is its simplicity. It is easy to use, portable, and does not require calibration or batteries. It is also affordable and reliable for quick checks.
However, it does not provide digital readings or very high precision. It is mainly used for comparison rather than exact measurement in microns.
Where Can You Get Quality Workshop Tools?
Jaibros is a reliable place for workshop and industrial tool needs because it focuses on quality, accuracy, and practical use. The platform offers a wide range of measuring and machining tools that are suitable for daily workshop work, inspection tasks, and training use. Products are clearly listed with proper details, making it easier for users to choose the right tool for their requirement. Jaibros is known for supporting machinists, technicians, and industries by providing tools that help improve measurement accuracy and work efficiency without confusion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main use of a radius gauge?
It is used to check and measure the radius of curved surfaces on mechanical parts.
2. What is the usual least count of this tool?
Most standard sets have a least count of 0.5 mm.
3. Can it measure both internal and external curves?
Yes, many sets are designed to check both concave and convex radii.
4. Is it suitable for CNC machining inspection?
Yes, it is commonly used for quick inspection in CNC and manual machining.
5. Does it need calibration like other measuring tools?
No, it does not require calibration as it works on direct curve matching.
Conclusion
A radius gauge is a basic yet essential inspection tool in mechanical and manufacturing work. It helps ensure curved surfaces are made accurately and consistently. Understanding its least count, size range, specifications, and correct usage improves measurement confidence and part quality.
For workshops, students, and inspectors, this tool remains a practical solution for quick and reliable radius checking.