Understanding Data Pipelines at a High Level
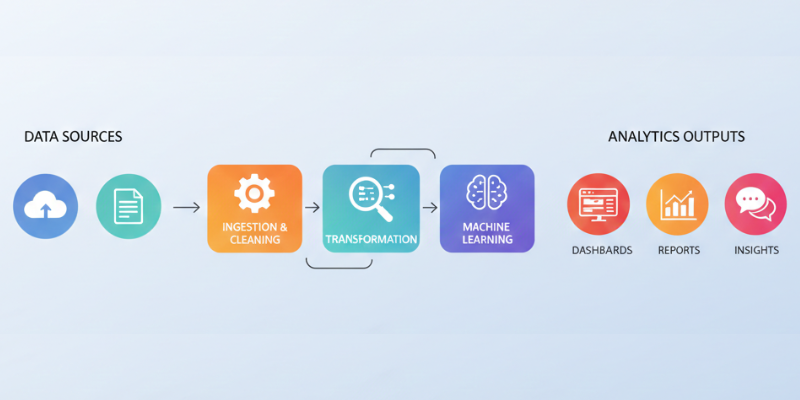
Organizations rely on smooth data movement to make informed decisions. This is where data pipelines play a critical role by enabling data to flow from multiple sources to usable destinations. At a high level, a data pipeline is a structured process that collects, processes, and delivers data so it can be analyzed effectively.
For those looking to establish a solid base in analytics, understanding this concept is essential, and if you are looking to strengthen these fundamentals, you may consider enrolling in Data Analytics Courses in Bangalore at FITA Academy to gain practical exposure and industry-oriented knowledge that supports real learning outcomes.
What a Data Pipeline Actually Does
A data pipeline ensures that raw data does not stay scattered or unused. It gathers data from different sources, such as applications, databases, or external systems, and moves it through a defined process. During this movement, data may be cleaned, organized, or structured to make it suitable for analysis. The goal is to deliver reliable and timely data to analysts, dashboards, or reporting tools without manual effort.
Core Components of a Data Pipeline
Every data pipeline is built using a few essential components that work together. The first component is the data source, where information originates. The second is data processing, where transformations such as filtering or formatting occur. The final component is the destination, which could be a data warehouse, analytics tool, or visualization platform. These components operate in sequence to maintain data consistency and accuracy throughout the pipeline.
Types of Data Pipelines
Data pipelines generally fall into two main types based on how data is processed. Batch pipelines move data in groups at scheduled intervals, which works well for historical reporting. Real-time pipelines process data continuously as it is generated, which is useful for monitoring and immediate insights.
Understanding these types helps analysts choose the right approach based on business needs, and learners exploring structured analytics training, such as a Data Analytics Course in Hyderabad often gain clarity on how and when each pipeline type is applied in real scenarios.
Why Data Pipelines Matter in Analytics
Without data pipelines, analytics becomes slow, error prone, and heavily dependent on manual work. Pipelines automate repetitive tasks and ensure that data arrives in a ready-to-use format. This allows analysts to focus more on discovering insights rather than preparing data. Consistent pipelines also improve data quality, which directly impacts the accuracy of reports and decisions made from them.
Common Challenges in Data Pipelines
Despite their benefits, data pipelines come with challenges that need careful handling. Data quality issues, system failures, and scaling problems can affect pipeline performance. Poorly designed pipelines may also introduce delays or inconsistencies. Addressing these challenges requires clear design, monitoring, and an understanding of how data behaves as it moves through different systems.
How Data Pipelines Support Business Growth
Reliable data pipelines help organizations respond faster to changes and opportunities. They provide decision makers with up-to-date information, enabling better planning and performance tracking. As businesses grow, pipelines also make it easier to handle increasing data volumes without disrupting operations. This makes them a foundational element of any mature data analytics strategy.
Understanding data pipelines at a high level helps beginners connect technical processes with real business value. These pipelines act as the backbone of analytics by ensuring data flows smoothly from source to insight. For those who want to deepen their understanding and apply these concepts confidently in real projects, taking a Data Analytics Course in Ahmedabad can be a practical step toward building strong analytics skills and advancing your career with structured learning support.
Also check: The Principle of Simplicity in Data Visualization






