Pura Peptides for Longevity and Wellness
Pure peptides are short chains of amino acids that are carefully synthesized and refined to remove impurities and unwanted compounds. These molecules Pure peptides an important role in modern science, medicine, and biotechnology because of their precise structure and predictable behavior. Scientists and researchers value purity in peptides because even small contaminants can affect experimental results or therapeutic effectiveness.
Peptides occur naturally in the human body, where they act as signaling molecules, hormones, and building blocks for proteins. However, “pure peptides” usually refer to laboratory-produced peptides that have undergone strict purification processes, often using advanced methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). This ensures that the final product contains only the intended amino acid sequence.
Why Purity Matters in Peptide Research
Purity is essential when peptides are used in scientific research or pharmaceutical development. In laboratories, researchers rely on highly accurate compounds to study biological processes, test drug interactions, and develop innovative treatments. Impurities can interfere with results, making experiments unreliable or difficult to reproduce.
For example, in drug development, pure peptides may be studied for their potential roles in hormone regulation, immune response, and tissue repair. Regulatory organizations such as the Food and Drug Administration emphasize strict quality standards for compounds used in clinical research. Ensuring peptide purity helps maintain safety, consistency, and scientific credibility.
Common Applications of Pure Peptides
Pure peptides are widely used across multiple fields. In medicine, they are studied for their potential therapeutic properties. Some peptides are already used in approved treatments for conditions like diabetes, osteoporosis, and hormonal disorders. Researchers continue exploring how peptides might support regenerative medicine and targeted drug delivery.
In biotechnology, pure peptides help scientists understand protein interactions and cellular communication. Because peptides can be synthesized with precise sequences, they allow researchers to examine biological mechanisms at a detailed level.
The cosmetic industry has also shown interest in peptides, especially in skincare formulations designed to support collagen production and skin elasticity. Although these applications differ from medical uses, purity still plays a key role in ensuring product stability and effectiveness.
How Pure Peptides Are Produced
Producing pure peptides requires advanced laboratory techniques. The most common method is solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), which allows scientists to build peptide chains step by step. After synthesis, purification processes remove incomplete sequences and by-products.
Quality testing follows purification to confirm the peptide’s identity and concentration. Analytical tools such as mass spectrometry and chromatography help verify that the peptide meets strict standards. International health organizations like the World Health Organization encourage strong laboratory practices to maintain safety and reliability in biomedical research.
The Future of Peptide Science
Peptide research continues to expand as scientists discover new ways these molecules can support healthcare innovation. Advances in biotechnology and molecular engineering are making peptide synthesis more efficient and cost-effective. This progress could lead to new treatments that are highly targeted and have fewer side effects than traditional drugs.
As interest in precision medicine grows, pure peptides are likely to play an increasingly important role in diagnostics, therapeutics, and scientific discovery. Their versatility, combined with strict purification standards, makes them valuable tools for researchers around the world.
In summary, pure peptides represent a critical component of modern scientific research and biotechnology. Their reliability, precision, and wide range of applications make them essential for advancing medicine and understanding biological systems.
Nach Verein filtern
Read More
"Detailed Analysis of Executive Summary Europe FTTH GPON Market Size and Share Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the FTTH GPON market will grow at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. When market research report is brilliant and precise, it proves to be a backbone for the business that helps to thrive in the competition. An all-inclusive Europe FTTH GPON...

Introduction to FUTBIN Podcast Episode 5 NepentheZ returns for episode five alongside Richard Buckley and MattFUTTrading, ready to discuss the latest updates in FC 26. The conversation covers Manchester United’s player ratings, offering insights into how the squad stacks up for the new game. New Icon cards are highlighted, with a special focus on Ibrahimovic’s stats and what his...

Global Demand Outlook for Executive Summary Cloud Gaming Market Size and Share The global cloud gaming market size was valued at USD 2.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 62.43 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 51.22% during the forecast period. This Cloud Gaming report includes a wide-ranging evaluation of the market’s growth prospects...

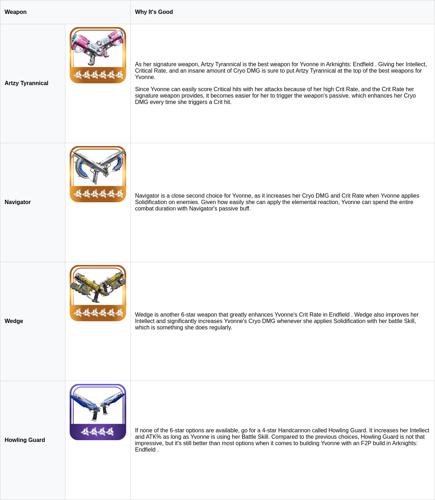
Yvonne Best is a powerful Cryo striker featured in Arknights: Endfield. Her combat style centers on executing a series of tactical skills that charge her ultimate ability. As her ultimate charges, her regular attacks become significantly more potent, unleashing devastating damage upon enemies. Additionally, Yvonne’s skill set emphasizes activating the solidification reaction, which is...
Personal Cooling Device Market Overview Zion Market Research has added a new research report to its extensive database of reports, titled " Personal Cooling Devices Market Size, Industry Trends, Historical Data, Growth Analysis, Forecast to 2032. " This comprehensive report provides an assessment of the global personal cooling devices market, including its projected growth rate over...


