Is Cold Laser Therapy Safe and Effective?
Cold laser therapy has gained significant attention in recent years. Many patients seek non-invasive treatments for chronic pain and injuries. This therapeutic approach uses low-level light to stimulate healing processes. Medical professionals increasingly recommend this treatment for various conditions.
Understanding Cold Laser Therapy Technology
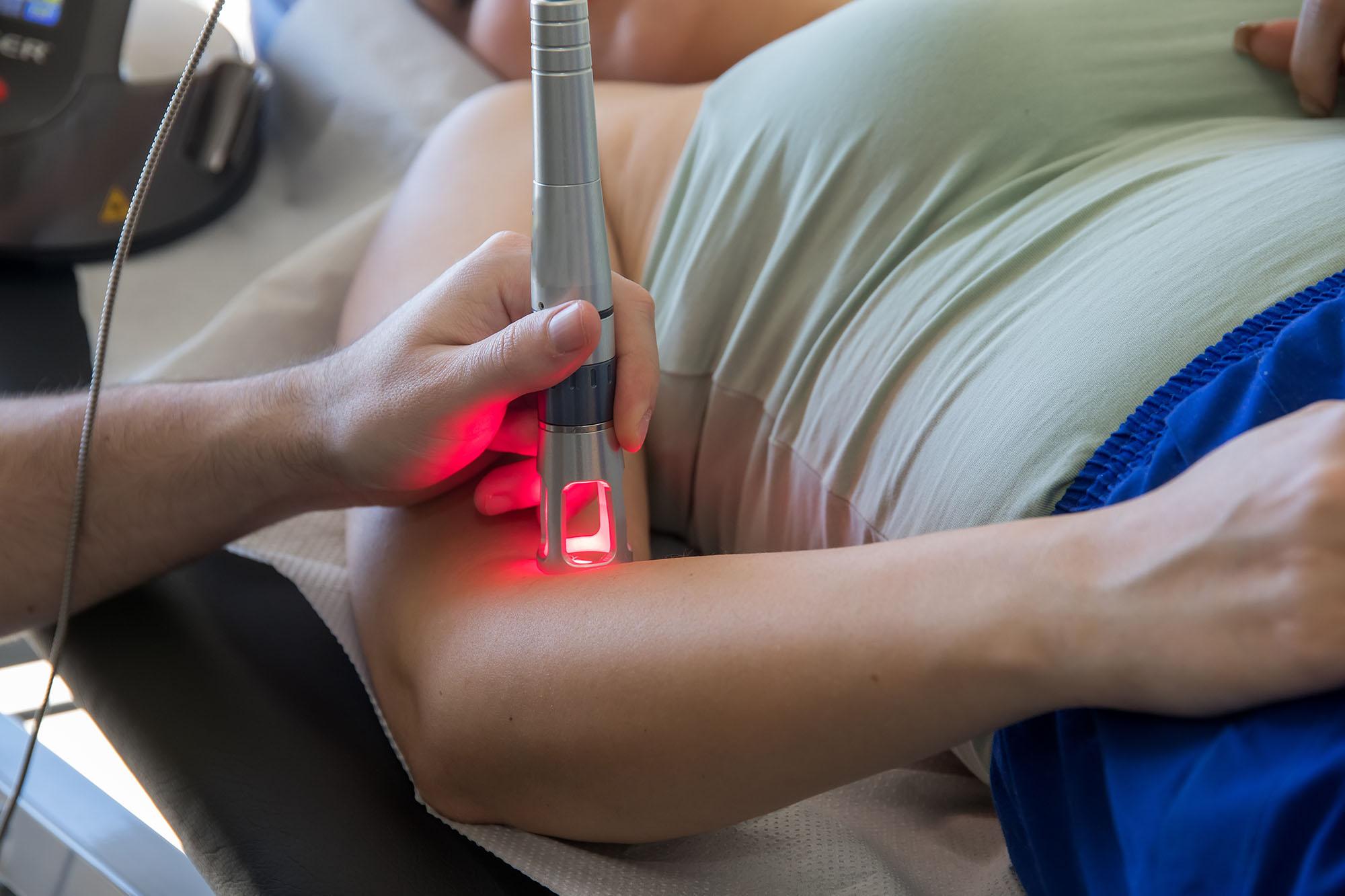
Low-level laser therapy operates through photobiomodulation mechanisms in tissues. The device emits specific wavelengths of light onto affected areas. These wavelengths typically range between 600 and 1000 nanometers. The light penetrates skin without generating heat or damaging cells.
Cellular mitochondria absorb the photons from the laser device. This absorption triggers increased ATP production within treated cells. Enhanced cellular energy accelerates natural healing and reduces inflammation significantly. The process occurs at a molecular level within tissues.
How Cold Laser Treatment Works in Practice
Healthcare providers position the laser device directly over injured areas. Treatment sessions typically last between five and twenty minutes total. Patients feel no pain, heat, or discomfort during sessions. The therapy requires multiple sessions for optimal therapeutic results.
Most treatment protocols involve two to three weekly sessions initially. A complete course usually spans four to six weeks overall. The cumulative effect builds progressively with each successive treatment session. Tissues respond gradually to the light energy exposure.
Safety Profile of Low-Level Laser Therapy
The FDA has cleared numerous cold laser devices for therapeutic use. These treatments demonstrate an excellent safety record across multiple studies. No significant adverse effects have been reported in clinical trials. The non-invasive nature eliminates risks associated with surgical interventions.
Unlike traditional surgical lasers, these devices don't cut or burn tissue. The low power output prevents any thermal damage to cells. Patients can resume normal activities immediately following each treatment session. There's no recovery period or downtime required after therapy.
Eye protection remains the primary safety consideration during treatment sessions. Practitioners and patients should avoid direct eye exposure to beams. Most clinics provide protective eyewear as a standard safety measure. When used properly, risks remain minimal and manageable.
Clinical Effectiveness for Pain Management
Numerous clinical studies support the effectiveness of cold laser therapy for pain. Research demonstrates significant pain reduction in osteoarthritis patients after treatment. Neck pain sufferers experience measurable improvement in mobility and comfort. Lower back pain responds particularly well to this therapeutic approach.
A systematic review examined over fifty randomized controlled trials recently. The analysis confirmed moderate to strong evidence for pain relief. Patients reported decreased pain intensity on standardized assessment scales. Functional improvements accompanied the reduction in pain symptoms.
Rheumatoid arthritis patients benefit from reduced joint inflammation and stiffness. Fibromyalgia sufferers report decreased tender points following treatment courses. Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms improve without surgical intervention required. The therapy addresses pain through multiple biological mechanisms simultaneously.
Effectiveness in Tissue Repair and Healing
Wound healing accelerates significantly with regular cold laser applications. The therapy promotes collagen synthesis essential for tissue repair. Increased circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to damaged areas. Cellular proliferation rates improve in treated wound sites.
Sports medicine practitioners use this therapy extensively for injuries. Muscle strains, ligament sprains, and tendon damage respond favorably. Inflammation decreases while tissue regeneration processes accelerate noticeably. Athletes experience faster return to training and competition schedules.
Dental applications show promising results for post-surgical healing and recovery. Periodontal disease treatment outcomes improve with adjunctive laser therapy. Temporomandibular joint disorders respond well to this treatment modality. Oral tissue healing occurs more rapidly following dental procedures.
Neurological and Nerve-Related Applications
Peripheral neuropathy patients experience symptom relief with consistent treatments. Diabetic neuropathy shows particular responsiveness to low-level laser applications. Nerve regeneration appears enhanced through photobiomodulation effects on tissue. Patients report decreased tingling, numbness, and burning sensations.
Nerve injury recovery improves when therapy begins soon after trauma. The treatment reduces nerve inflammation and promotes axonal regeneration. Carpal tunnel syndrome responds without needing surgical decompression procedures. Sciatic nerve pain diminishes through targeted treatment of affected areas.
Limitations and Realistic Expectations
Cold laser therapy works best as part of comprehensive treatment plans. It should complement, not replace, other evidence-based medical interventions. Results vary significantly based on individual patient factors and conditions. Age, overall health, and condition severity influence treatment outcomes.
Some conditions respond better than others to this therapeutic approach. Acute injuries typically show faster improvement than chronic conditions. Superficial tissues respond more readily than deeply located structures. Patient commitment to full treatment protocols affects success rates.
The therapy may not work equally well for everyone. Some patients experience dramatic improvements while others notice minimal changes. Setting realistic expectations prevents disappointment with treatment outcomes. Healthcare providers should discuss probable results before beginning therapy.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
Treatment costs vary widely depending on geographic location and provider. Individual sessions typically range from fifty to two hundred dollars. Complete treatment courses may cost several hundred to thousands total. Many insurance plans don't cover cold laser therapy currently.
Some providers offer package deals reducing per-session costs significantly. Medicare doesn't typically reimburse for cold laser treatments yet. Private insurance coverage depends on specific plan policies and restrictions. Patients should verify coverage details before beginning treatment protocols.
Despite out-of-pocket expenses, many patients consider therapy cost-effective long-term. Avoiding surgery or prolonged medication use provides substantial savings. The non-invasive nature eliminates hospital and anesthesia expenses entirely. Quality of life improvements justify costs for many patients.
Choosing a Qualified Provider
Selecting properly trained practitioners ensures safe and effective treatment delivery. Physical therapists, chiropractors, and physicians commonly offer this therapy. Verify that providers have specific training in laser therapy protocols. Equipment quality significantly impacts treatment effectiveness and safety.
Ask about the specific laser device brand and FDA clearance. Reputable manufacturers provide evidence-based treatment protocols and guidelines. Experience treating your specific condition matters tremendously for outcomes. Request information about success rates with similar patient cases.
The Future of Cold Laser Therapy
Ongoing research continues expanding our understanding of therapeutic mechanisms. New applications emerge regularly as scientists study different conditions. Device technology improves with more targeted wavelengths and delivery systems. Clinical acceptance grows as evidence accumulates supporting various applications.
Cold laser therapy represents a safe, non-invasive treatment option. The effectiveness varies depending on specific conditions and patient factors. Most patients experience no adverse effects during or after treatments. Research supports its use for pain management and tissue healing. This therapeutic approach deserves consideration as part of comprehensive care plans.






