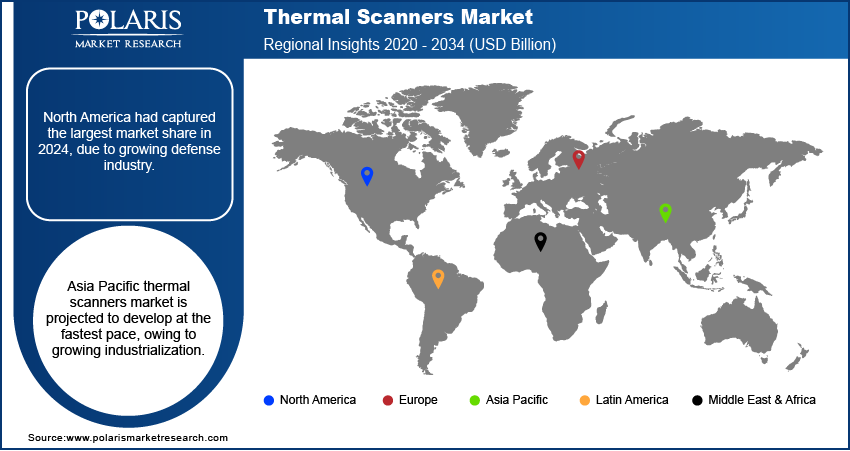
The global thermal scanners market size was valued at USD 5.58 billion in 2024. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.50% during 2025 to 2034.
The global thermal scanners market is witnessing strong growth as industries, governments, and healthcare institutions increasingly adopt thermal imaging technology for safety, security, and diagnostic applications. These systems—designed to detect infrared energy and convert it into temperature readings or thermal images—have become essential in modern infrastructure, especially in the wake of heightened health and security awareness. The demand for accurate, non-contact temperature measurement and enhanced surveillance capabilities continues to drive innovation and adoption across multiple sectors.
Market Overview
Thermal scanners are devices that measure surface temperature variations using infrared radiation. They are widely used for applications in industrial inspection, defense surveillance, healthcare diagnostics, building maintenance, and airport screening. The technology plays a critical role in detecting heat patterns that are invisible to the naked eye, allowing users to identify anomalies, prevent failures, and ensure safety.
The market has evolved rapidly due to advances in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and image-processing algorithms. Modern scanners offer higher resolution, faster frame rates, and integration with cloud and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms. These developments are enabling precise temperature mapping and automated monitoring across both fixed and portable devices.
Growing concerns over workplace safety, along with the expansion of automation and predictive maintenance programs, are key drivers behind the adoption of thermal scanners. In industrial environments, they help detect equipment overheating, electrical faults, and process irregularities before they escalate into costly failures. Similarly, in healthcare and public safety, thermal imaging systems have proven invaluable for mass temperature screening and diagnostic imaging, ensuring efficient disease prevention and control.
As industries transition toward smart manufacturing and connected security systems, the integration of thermal imaging with digital analytics and wireless networks is expected to shape the future of the market.
Browse More Insights: https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/thermal-scanner-market
Market Segmentation
The global thermal scanners market can be segmented by type, wavelength, application, and end-use industry.
1. By Type:
Handheld Thermal Scanners: Portable devices used by technicians, security personnel, and healthcare professionals for quick, on-site thermal inspections. They are valued for their flexibility and ease of use.
Fixed or Mounted Thermal Scanners: Installed in buildings, airports, production facilities, and surveillance systems for continuous temperature monitoring and automation.
Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Thermal Cameras: Provide wide-area coverage with remote-controlled viewing angles, commonly used in perimeter security and traffic monitoring.
2. By Wavelength:
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR): Suitable for imaging through glass and detecting high-temperature materials like metals and ceramics.
Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR): Offers high sensitivity and is used in scientific research, defense, and industrial applications.
Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR): Ideal for non-contact temperature measurements and widely used in medical and surveillance systems.
3. By Application:
Industrial Inspection: Used in predictive maintenance, process control, and electrical diagnostics to prevent system failures.
Security and Surveillance: Enables night vision and intrusion detection in defense, transportation, and border control.
Healthcare and Screening: Utilized for non-invasive body temperature screening and diagnostic imaging.
Automotive and Transportation: Integrated into driver-assistance systems for pedestrian detection and enhanced visibility in low-light conditions.
Building and Construction: Employed to detect heat leaks, insulation failures, and energy inefficiencies.
4. By End-Use Industry:
Healthcare: For patient monitoring and thermal screening in hospitals and clinics.
Manufacturing: To monitor machinery temperature and ensure production safety.
Defense and Aerospace: For target acquisition, surveillance, and situational awareness.
Commercial and Public Infrastructure: Used in airports, offices, and public spaces for safety screening and energy management.
Automotive: For safety and thermal sensing applications in electric vehicles and autonomous systems.
The wide range of applications underscores the versatility of thermal scanners across different industries, reinforcing their importance in modern operational environments.
The global thermal scanners market is witnessing strong growth as industries, governments, and healthcare institutions increasingly adopt thermal imaging technology for safety, security, and diagnostic applications. These systems—designed to detect infrared energy and convert it into temperature readings or thermal images—have become essential in modern infrastructure, especially in the wake of heightened health and security awareness. The demand for accurate, non-contact temperature measurement and enhanced surveillance capabilities continues to drive innovation and adoption across multiple sectors.
Market Overview
Thermal scanners are devices that measure surface temperature variations using infrared radiation. They are widely used for applications in industrial inspection, defense surveillance, healthcare diagnostics, building maintenance, and airport screening. The technology plays a critical role in detecting heat patterns that are invisible to the naked eye, allowing users to identify anomalies, prevent failures, and ensure safety.
The market has evolved rapidly due to advances in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and image-processing algorithms. Modern scanners offer higher resolution, faster frame rates, and integration with cloud and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms. These developments are enabling precise temperature mapping and automated monitoring across both fixed and portable devices.
Growing concerns over workplace safety, along with the expansion of automation and predictive maintenance programs, are key drivers behind the adoption of thermal scanners. In industrial environments, they help detect equipment overheating, electrical faults, and process irregularities before they escalate into costly failures. Similarly, in healthcare and public safety, thermal imaging systems have proven invaluable for mass temperature screening and diagnostic imaging, ensuring efficient disease prevention and control.
As industries transition toward smart manufacturing and connected security systems, the integration of thermal imaging with digital analytics and wireless networks is expected to shape the future of the market.
Browse More Insights: https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/thermal-scanner-market
Market Segmentation
The global thermal scanners market can be segmented by type, wavelength, application, and end-use industry.
1. By Type:
Handheld Thermal Scanners: Portable devices used by technicians, security personnel, and healthcare professionals for quick, on-site thermal inspections. They are valued for their flexibility and ease of use.
Fixed or Mounted Thermal Scanners: Installed in buildings, airports, production facilities, and surveillance systems for continuous temperature monitoring and automation.
Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Thermal Cameras: Provide wide-area coverage with remote-controlled viewing angles, commonly used in perimeter security and traffic monitoring.
2. By Wavelength:
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR): Suitable for imaging through glass and detecting high-temperature materials like metals and ceramics.
Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR): Offers high sensitivity and is used in scientific research, defense, and industrial applications.
Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR): Ideal for non-contact temperature measurements and widely used in medical and surveillance systems.
3. By Application:
Industrial Inspection: Used in predictive maintenance, process control, and electrical diagnostics to prevent system failures.
Security and Surveillance: Enables night vision and intrusion detection in defense, transportation, and border control.
Healthcare and Screening: Utilized for non-invasive body temperature screening and diagnostic imaging.
Automotive and Transportation: Integrated into driver-assistance systems for pedestrian detection and enhanced visibility in low-light conditions.
Building and Construction: Employed to detect heat leaks, insulation failures, and energy inefficiencies.
4. By End-Use Industry:
Healthcare: For patient monitoring and thermal screening in hospitals and clinics.
Manufacturing: To monitor machinery temperature and ensure production safety.
Defense and Aerospace: For target acquisition, surveillance, and situational awareness.
Commercial and Public Infrastructure: Used in airports, offices, and public spaces for safety screening and energy management.
Automotive: For safety and thermal sensing applications in electric vehicles and autonomous systems.
The wide range of applications underscores the versatility of thermal scanners across different industries, reinforcing their importance in modern operational environments.
The global thermal scanners market size was valued at USD 5.58 billion in 2024. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.50% during 2025 to 2034.
The global thermal scanners market is witnessing strong growth as industries, governments, and healthcare institutions increasingly adopt thermal imaging technology for safety, security, and diagnostic applications. These systems—designed to detect infrared energy and convert it into temperature readings or thermal images—have become essential in modern infrastructure, especially in the wake of heightened health and security awareness. The demand for accurate, non-contact temperature measurement and enhanced surveillance capabilities continues to drive innovation and adoption across multiple sectors.
Market Overview
Thermal scanners are devices that measure surface temperature variations using infrared radiation. They are widely used for applications in industrial inspection, defense surveillance, healthcare diagnostics, building maintenance, and airport screening. The technology plays a critical role in detecting heat patterns that are invisible to the naked eye, allowing users to identify anomalies, prevent failures, and ensure safety.
The market has evolved rapidly due to advances in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and image-processing algorithms. Modern scanners offer higher resolution, faster frame rates, and integration with cloud and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms. These developments are enabling precise temperature mapping and automated monitoring across both fixed and portable devices.
Growing concerns over workplace safety, along with the expansion of automation and predictive maintenance programs, are key drivers behind the adoption of thermal scanners. In industrial environments, they help detect equipment overheating, electrical faults, and process irregularities before they escalate into costly failures. Similarly, in healthcare and public safety, thermal imaging systems have proven invaluable for mass temperature screening and diagnostic imaging, ensuring efficient disease prevention and control.
As industries transition toward smart manufacturing and connected security systems, the integration of thermal imaging with digital analytics and wireless networks is expected to shape the future of the market.
Browse More Insights: https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/thermal-scanner-market
Market Segmentation
The global thermal scanners market can be segmented by type, wavelength, application, and end-use industry.
1. By Type:
Handheld Thermal Scanners: Portable devices used by technicians, security personnel, and healthcare professionals for quick, on-site thermal inspections. They are valued for their flexibility and ease of use.
Fixed or Mounted Thermal Scanners: Installed in buildings, airports, production facilities, and surveillance systems for continuous temperature monitoring and automation.
Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Thermal Cameras: Provide wide-area coverage with remote-controlled viewing angles, commonly used in perimeter security and traffic monitoring.
2. By Wavelength:
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR): Suitable for imaging through glass and detecting high-temperature materials like metals and ceramics.
Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR): Offers high sensitivity and is used in scientific research, defense, and industrial applications.
Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR): Ideal for non-contact temperature measurements and widely used in medical and surveillance systems.
3. By Application:
Industrial Inspection: Used in predictive maintenance, process control, and electrical diagnostics to prevent system failures.
Security and Surveillance: Enables night vision and intrusion detection in defense, transportation, and border control.
Healthcare and Screening: Utilized for non-invasive body temperature screening and diagnostic imaging.
Automotive and Transportation: Integrated into driver-assistance systems for pedestrian detection and enhanced visibility in low-light conditions.
Building and Construction: Employed to detect heat leaks, insulation failures, and energy inefficiencies.
4. By End-Use Industry:
Healthcare: For patient monitoring and thermal screening in hospitals and clinics.
Manufacturing: To monitor machinery temperature and ensure production safety.
Defense and Aerospace: For target acquisition, surveillance, and situational awareness.
Commercial and Public Infrastructure: Used in airports, offices, and public spaces for safety screening and energy management.
Automotive: For safety and thermal sensing applications in electric vehicles and autonomous systems.
The wide range of applications underscores the versatility of thermal scanners across different industries, reinforcing their importance in modern operational environments.
0 Commenti
·0 condivisioni
·9K Views
·0 Anteprima