ISO 22000 Certification: Ensuring Excellence in Food Safety Management
What Is ISO 22000 Certification?
ISO 22000 certification confirms that an organization has implemented a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) that complies with the requirements of ISO 22000. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization, this internationally recognized standard provides a structured framework for identifying, controlling, and preventing food safety hazards across the entire supply chain. It integrates the principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) with a management system approach, ensuring food safety is systematically managed rather than treated as a one-time inspection process. ISO 22000 applies to all organizations in the food chain, including producers, processors, manufacturers, transporters, packaging companies, storage providers, and retailers.
Why ISO 22000 Certification Is Important
Food safety is a global concern, and any failure can result in serious health risks, financial losses, and reputational damage. ISO 22000 certification demonstrates that a company has implemented preventive controls to manage biological, chemical, and physical hazards effectively. It builds trust among customers, regulators, suppliers, and business partners by showing a clear commitment to food safety and compliance. In many markets, certification enhances access to international trade opportunities and strengthens competitiveness. More importantly, it creates confidence that products are consistently produced and handled under controlled and safe conditions.
Core Requirements of ISO 22000
ISO 22000 requires organizations to establish a comprehensive food safety management system built on several key elements. These include interactive communication throughout the food chain, systematic management processes, prerequisite programs (PRPs), and a thorough hazard analysis. Organizations must identify potential hazards, evaluate associated risks, and implement control measures such as critical control points (CCPs). Clear documentation, defined responsibilities, employee training, and emergency preparedness are also mandatory components. The standard emphasizes risk-based thinking and continuous improvement, ensuring that food safety measures evolve in response to changing operational and regulatory conditions.
The Certification Process
The journey to ISO 22000 certification typically begins with a gap analysis to assess current food safety practices against the standard’s requirements. Organizations then develop policies, procedures, and monitoring systems aligned with ISO 22000. Staff training ensures employees understand food safety responsibilities and compliance expectations. Once the system is fully implemented, an accredited certification body conducts a two-stage audit. The first stage reviews documentation and preparedness, while the second stage evaluates on-site implementation and effectiveness. If all requirements are met, certification is granted. Surveillance audits are conducted annually to maintain compliance, with recertification required every three years.
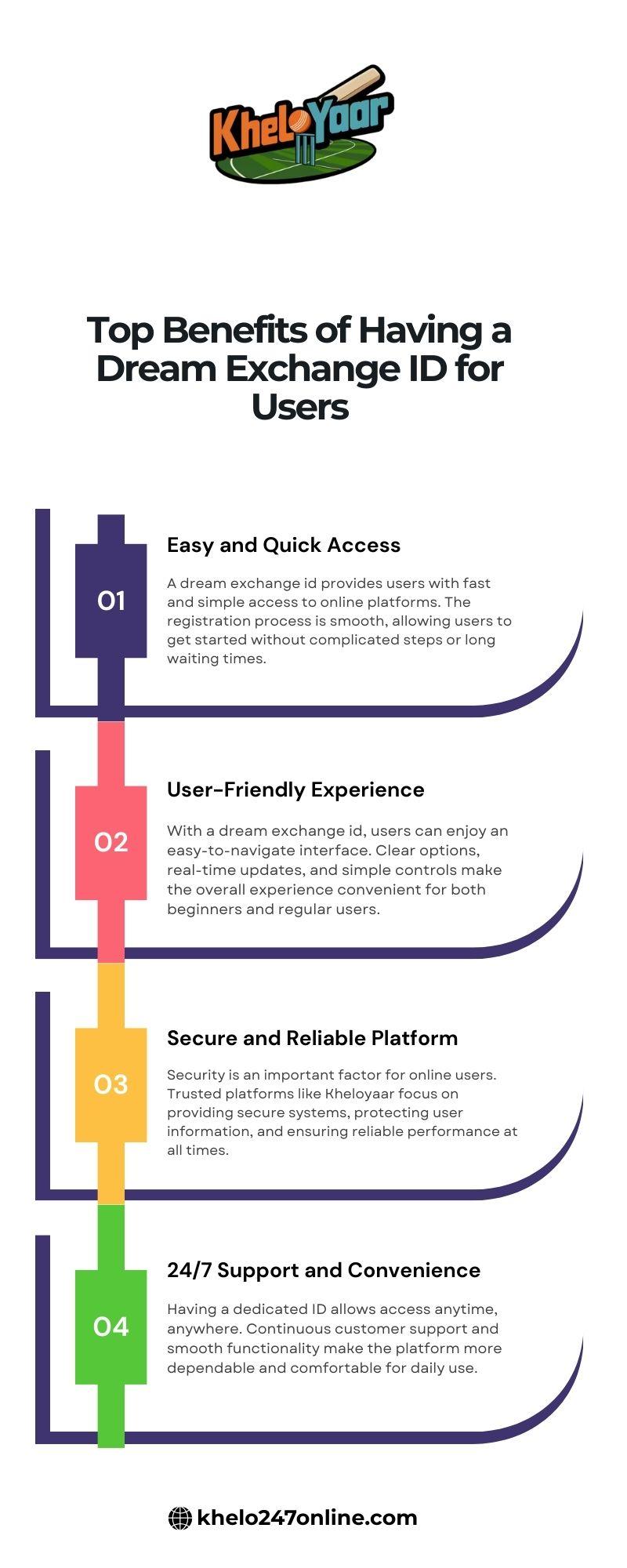
Benefits for Food Businesses
ISO 22000 certification provides both operational and strategic advantages. It improves internal efficiency by standardizing processes and reducing the likelihood of contamination or product recalls. Traceability systems enhance transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. Certification also strengthens brand reputation and increases customer confidence, particularly in highly regulated markets. Many retailers and distributors prefer suppliers with recognized food safety certifications, making ISO 22000 a valuable competitive asset.
Supporting Sustainable Growth and Consumer Trust
ISO 22000 certification is more than a regulatory requirement—it is a strategic investment in long-term business resilience. By embedding food safety into everyday operations, organizations protect public health while safeguarding their brand integrity. In a world where consumers demand transparency and accountability, ISO 22000 provides a reliable framework for consistent quality and safety. Ultimately, it supports sustainable growth, regulatory compliance, and enduring trust within the global food industry.
Web: https://iasiso-europe.com/french/iso-22000-certification-en-france/
What Is ISO 22000 Certification?
ISO 22000 certification confirms that an organization has implemented a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) that complies with the requirements of ISO 22000. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization, this internationally recognized standard provides a structured framework for identifying, controlling, and preventing food safety hazards across the entire supply chain. It integrates the principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) with a management system approach, ensuring food safety is systematically managed rather than treated as a one-time inspection process. ISO 22000 applies to all organizations in the food chain, including producers, processors, manufacturers, transporters, packaging companies, storage providers, and retailers.
Why ISO 22000 Certification Is Important
Food safety is a global concern, and any failure can result in serious health risks, financial losses, and reputational damage. ISO 22000 certification demonstrates that a company has implemented preventive controls to manage biological, chemical, and physical hazards effectively. It builds trust among customers, regulators, suppliers, and business partners by showing a clear commitment to food safety and compliance. In many markets, certification enhances access to international trade opportunities and strengthens competitiveness. More importantly, it creates confidence that products are consistently produced and handled under controlled and safe conditions.
Core Requirements of ISO 22000
ISO 22000 requires organizations to establish a comprehensive food safety management system built on several key elements. These include interactive communication throughout the food chain, systematic management processes, prerequisite programs (PRPs), and a thorough hazard analysis. Organizations must identify potential hazards, evaluate associated risks, and implement control measures such as critical control points (CCPs). Clear documentation, defined responsibilities, employee training, and emergency preparedness are also mandatory components. The standard emphasizes risk-based thinking and continuous improvement, ensuring that food safety measures evolve in response to changing operational and regulatory conditions.
The Certification Process
The journey to ISO 22000 certification typically begins with a gap analysis to assess current food safety practices against the standard’s requirements. Organizations then develop policies, procedures, and monitoring systems aligned with ISO 22000. Staff training ensures employees understand food safety responsibilities and compliance expectations. Once the system is fully implemented, an accredited certification body conducts a two-stage audit. The first stage reviews documentation and preparedness, while the second stage evaluates on-site implementation and effectiveness. If all requirements are met, certification is granted. Surveillance audits are conducted annually to maintain compliance, with recertification required every three years.
Benefits for Food Businesses
ISO 22000 certification provides both operational and strategic advantages. It improves internal efficiency by standardizing processes and reducing the likelihood of contamination or product recalls. Traceability systems enhance transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. Certification also strengthens brand reputation and increases customer confidence, particularly in highly regulated markets. Many retailers and distributors prefer suppliers with recognized food safety certifications, making ISO 22000 a valuable competitive asset.
Supporting Sustainable Growth and Consumer Trust
ISO 22000 certification is more than a regulatory requirement—it is a strategic investment in long-term business resilience. By embedding food safety into everyday operations, organizations protect public health while safeguarding their brand integrity. In a world where consumers demand transparency and accountability, ISO 22000 provides a reliable framework for consistent quality and safety. Ultimately, it supports sustainable growth, regulatory compliance, and enduring trust within the global food industry.
Web: https://iasiso-europe.com/french/iso-22000-certification-en-france/
ISO 22000 Certification: Ensuring Excellence in Food Safety Management
What Is ISO 22000 Certification?
ISO 22000 certification confirms that an organization has implemented a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) that complies with the requirements of ISO 22000. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization, this internationally recognized standard provides a structured framework for identifying, controlling, and preventing food safety hazards across the entire supply chain. It integrates the principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) with a management system approach, ensuring food safety is systematically managed rather than treated as a one-time inspection process. ISO 22000 applies to all organizations in the food chain, including producers, processors, manufacturers, transporters, packaging companies, storage providers, and retailers.
Why ISO 22000 Certification Is Important
Food safety is a global concern, and any failure can result in serious health risks, financial losses, and reputational damage. ISO 22000 certification demonstrates that a company has implemented preventive controls to manage biological, chemical, and physical hazards effectively. It builds trust among customers, regulators, suppliers, and business partners by showing a clear commitment to food safety and compliance. In many markets, certification enhances access to international trade opportunities and strengthens competitiveness. More importantly, it creates confidence that products are consistently produced and handled under controlled and safe conditions.
Core Requirements of ISO 22000
ISO 22000 requires organizations to establish a comprehensive food safety management system built on several key elements. These include interactive communication throughout the food chain, systematic management processes, prerequisite programs (PRPs), and a thorough hazard analysis. Organizations must identify potential hazards, evaluate associated risks, and implement control measures such as critical control points (CCPs). Clear documentation, defined responsibilities, employee training, and emergency preparedness are also mandatory components. The standard emphasizes risk-based thinking and continuous improvement, ensuring that food safety measures evolve in response to changing operational and regulatory conditions.
The Certification Process
The journey to ISO 22000 certification typically begins with a gap analysis to assess current food safety practices against the standard’s requirements. Organizations then develop policies, procedures, and monitoring systems aligned with ISO 22000. Staff training ensures employees understand food safety responsibilities and compliance expectations. Once the system is fully implemented, an accredited certification body conducts a two-stage audit. The first stage reviews documentation and preparedness, while the second stage evaluates on-site implementation and effectiveness. If all requirements are met, certification is granted. Surveillance audits are conducted annually to maintain compliance, with recertification required every three years.
Benefits for Food Businesses
ISO 22000 certification provides both operational and strategic advantages. It improves internal efficiency by standardizing processes and reducing the likelihood of contamination or product recalls. Traceability systems enhance transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. Certification also strengthens brand reputation and increases customer confidence, particularly in highly regulated markets. Many retailers and distributors prefer suppliers with recognized food safety certifications, making ISO 22000 a valuable competitive asset.
Supporting Sustainable Growth and Consumer Trust
ISO 22000 certification is more than a regulatory requirement—it is a strategic investment in long-term business resilience. By embedding food safety into everyday operations, organizations protect public health while safeguarding their brand integrity. In a world where consumers demand transparency and accountability, ISO 22000 provides a reliable framework for consistent quality and safety. Ultimately, it supports sustainable growth, regulatory compliance, and enduring trust within the global food industry.
Web: https://iasiso-europe.com/french/iso-22000-certification-en-france/
0 Reacties
·0 aandelen
·82 Views
·0 voorbeeld